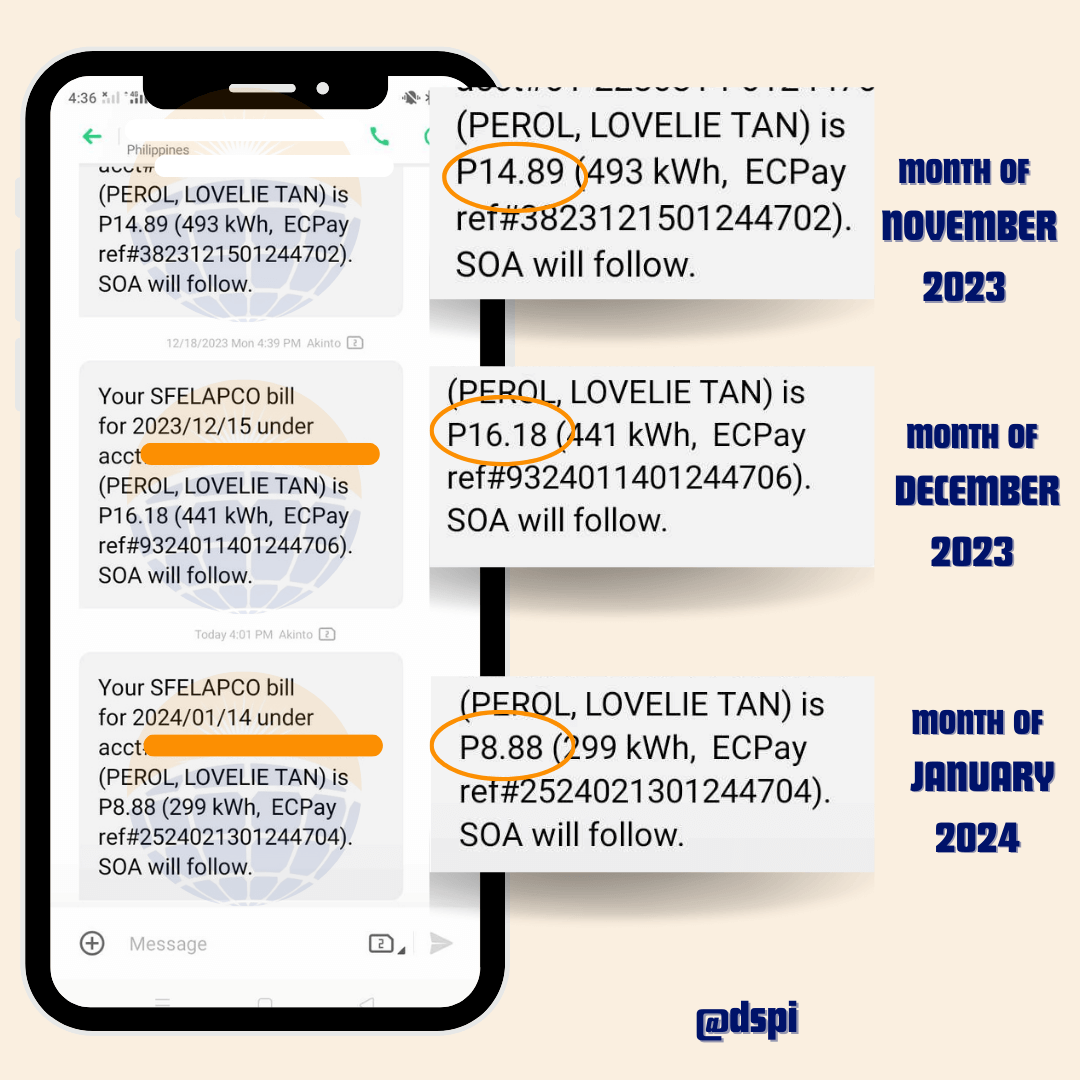
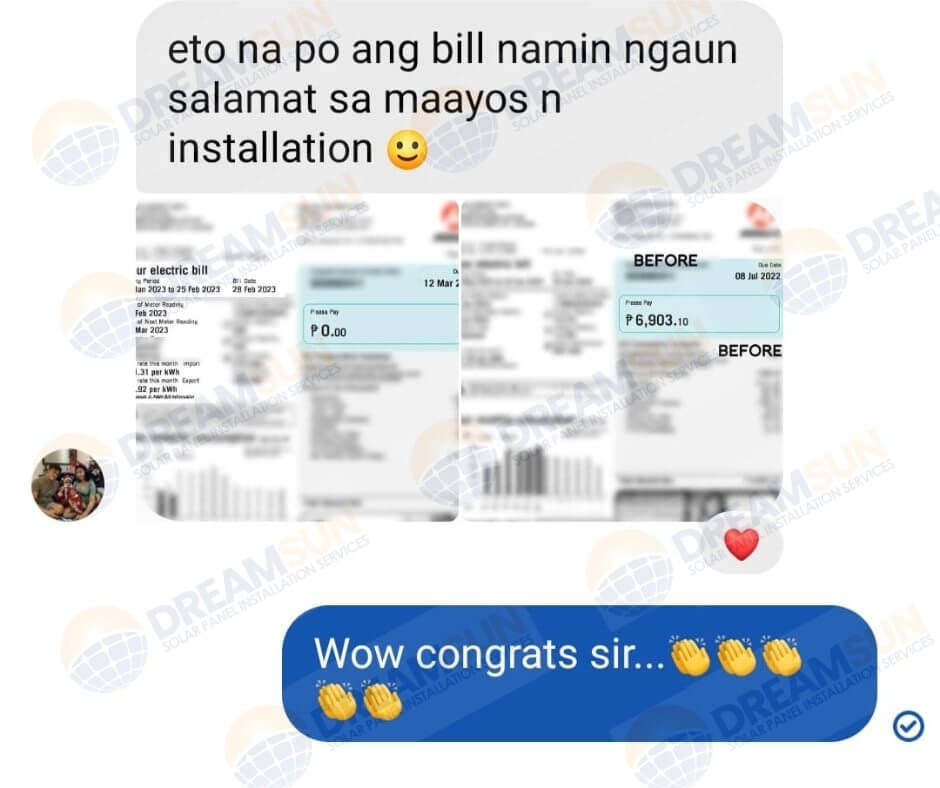
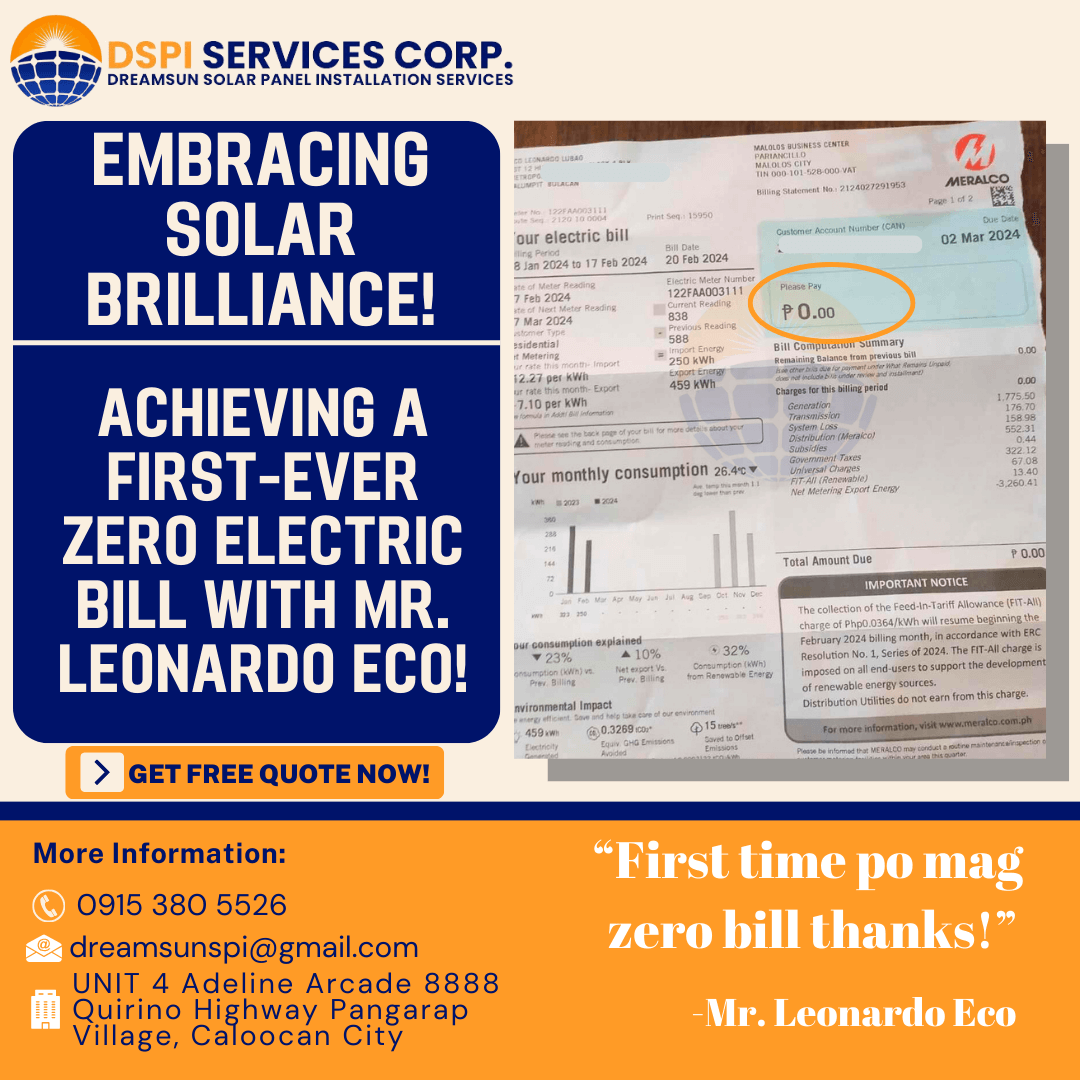
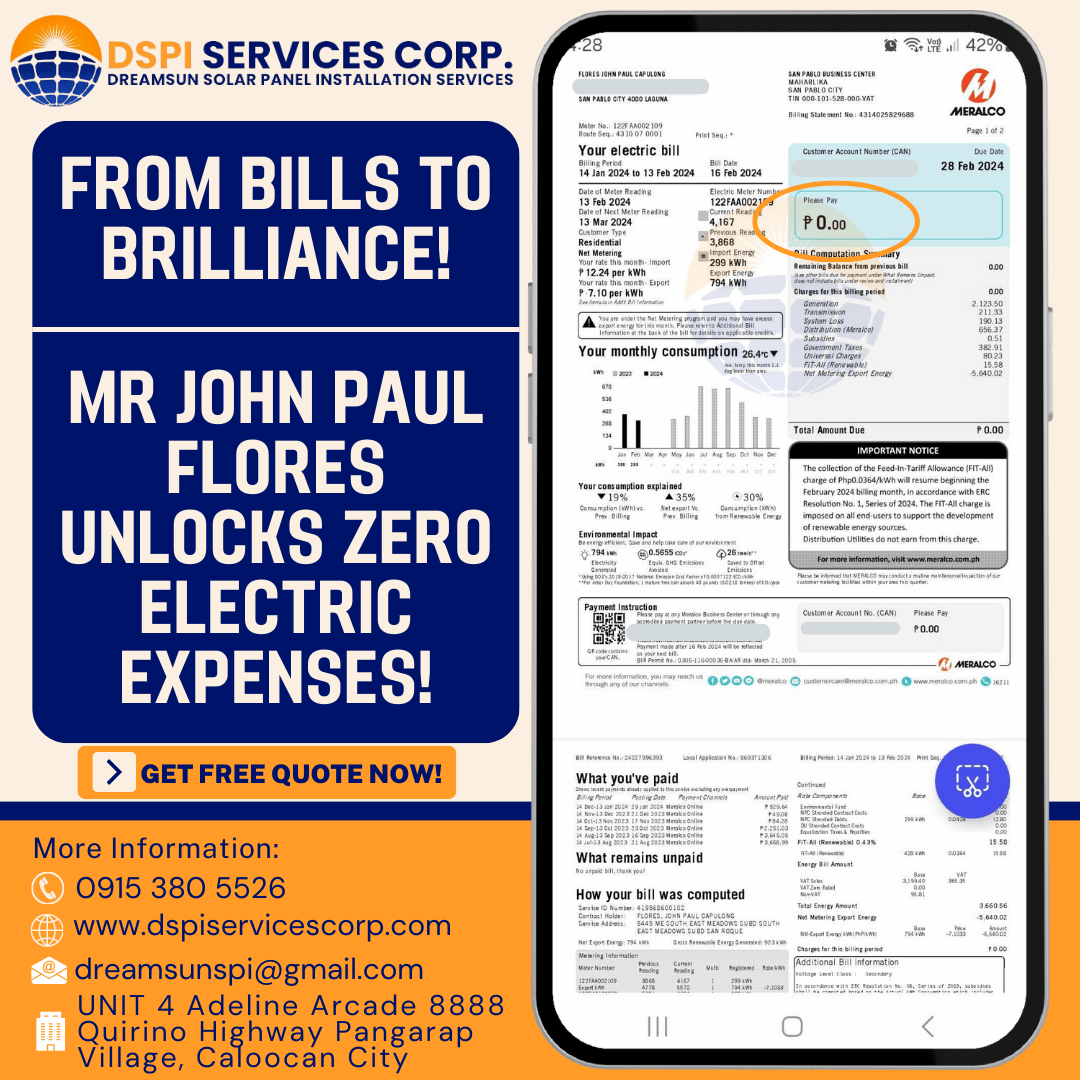
A grid-tied solar power system, also known as grid-connected or grid- interconnected system, is a type of solar PV system that is connected to the electrical grid.
Services
Solar Panel Installation
Grid-tied Solar Power System
- Solar Panels: The system consists of solar panels installed on the roof or property, which capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
- Inverter: The generated DC (direct current) electricity from the solar panels is then converted into AC (alternating current) electricity using an inverter. This AC electricity is compatible with the electrical grid and can be used to power appliances, lights, and other electrical devices in your home or business.
- Grid Connection: The AC electricity produced by the solar panels is fed into your property’s main electrical panel and distributed to power your electrical loads. Any excess electricity that is not immediately consumed by your property is automatically exported to the electrical grid.
- Net Metering: In many grid-tied systems, net metering is employed. This means that when your solar system generates more electricity than you need, the excess is sent back to the grid, and you receive credits for it on your electricity bill. During times when your solar system isn’t producing enough electricity (e.g., at night or on cloudy days), you can draw electricity from the grid as usual.
- Reduced Electricity Bills: By generating your own electricity from solar energy, you can significantly reduce or even eliminate your reliance on electricity from the grid. This can lead to substantial savings on your electricity bills over the long term.
- Environmental Benefits: Grid-tied solar systems produce clean, renewable energy from sunlight, reducing the need for electricity generated from fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. This helps lower greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
- Government Incentives: The Philippines offers various financial incentives to promote solar energy adoption, including net metering, which allows solar system owners to offset their electricity consumption with the excess energy they generate.
- Energy Independence: By generating your own electricity onsite, you become less reliant on the electrical grid and more self-sufficient in meeting your energy needs. This can provide greater energy security and resilience, especially during power outages or emergencies.
- Increased Property Value: Grid-tied solar power systems can increase the value of your property by reducing its operating costs and enhancing its appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
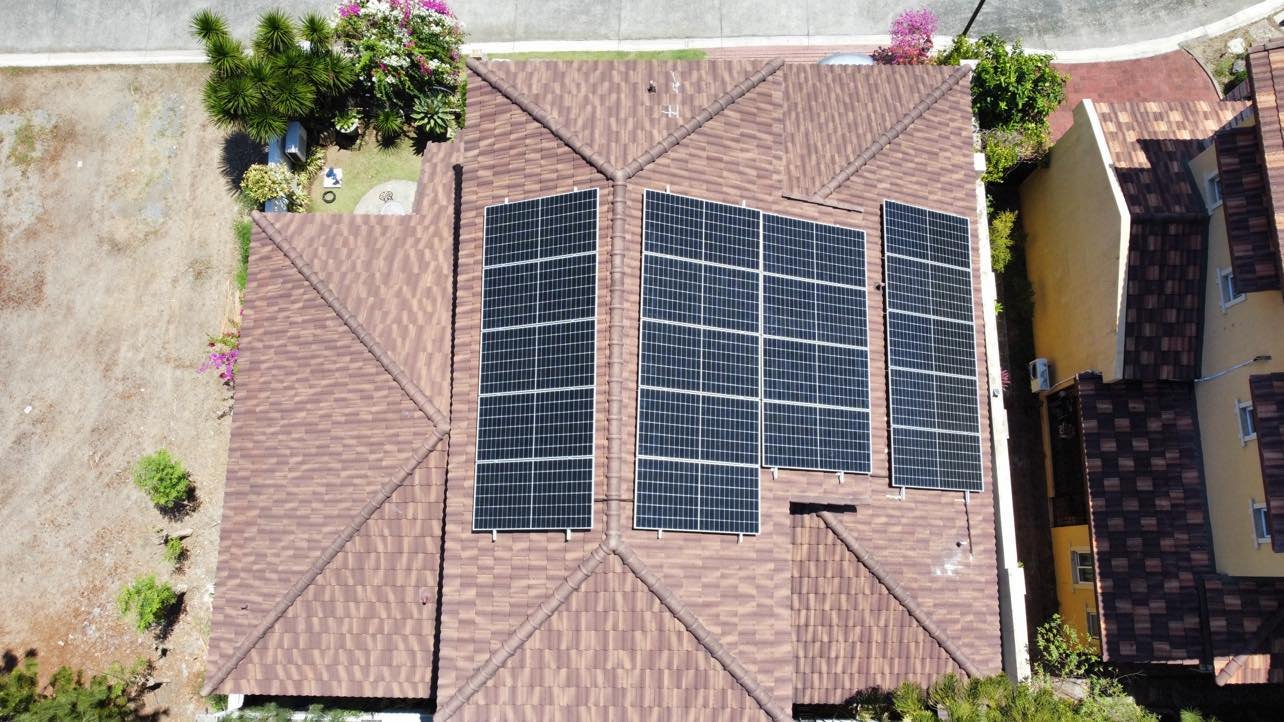
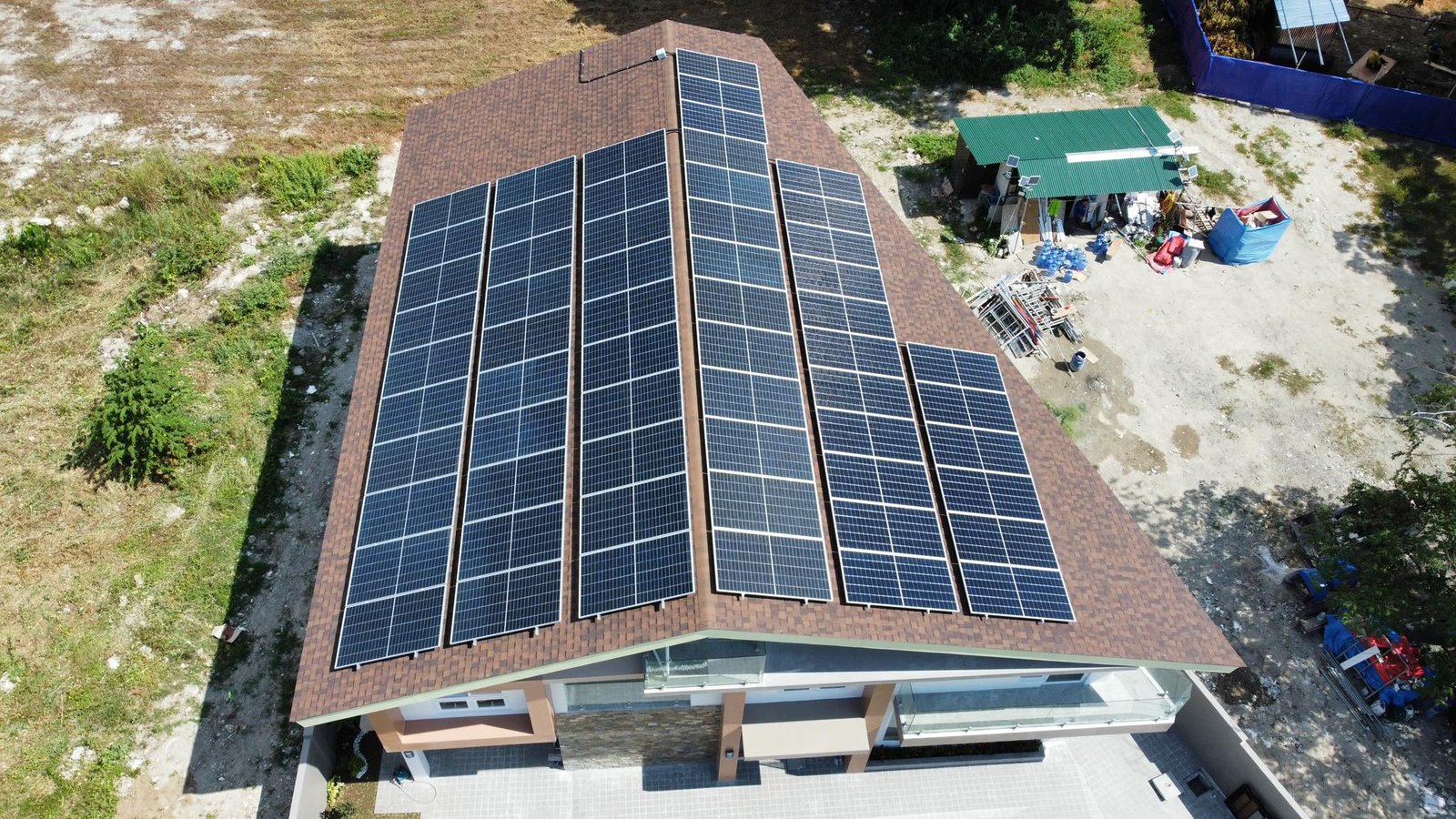


Hybrid Solar Power System
A hybrid solar power system combines the features of both grid-tied and off-grid solar systems, offering greater flexibility and reliability in meeting your energy needs.
- Solar Panels: Similar to a grid-tied system, hybrid systems utilize solar panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through photovoltaic technology.
- Battery Storage: In addition to solar panels, hybrid systems incorporate battery storage to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use during periods of low sunlight or at night. This allows you to maximize self-consumption of solar energy and reduce reliance on the grid.
- Inverter and Charge Controller: Hybrid systems are equipped with a hybrid inverter, which not only converts DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity for use in your home but also manages the charging and discharging of the battery bank. A charge controller regulates the flow of electricity between the solar panels, batteries, and loads to ensure efficient and safe operation.
- Grid Connection (Optional): While hybrid systems can operate independently of the grid, they can also be connected to the grid as a backup power source. In the event of prolonged periods of low sunlight or battery depletion, the system can draw electricity from the grid to supplement its power supply.
- Increased Energy Independence: Hybrid systems offer greater energy independence by enabling you to generate, store, and consume your own electricity onsite. This reduces your reliance on the grid and provides a reliable source of power, particularly in areas with unreliable grid infrastructure.
- 24/7 Power Availability: With battery storage, hybrid systems can provide power even when solar generation is insufficient, such as during nighttime or cloudy weather. This ensures uninterrupted electricity supply for essential loads, critical equipment, or during power outages.
- Optimized Self-Consumption: By storing excess solar energy in batteries for later use, hybrid systems allow you to maximize self-consumption of solar power and minimize reliance on grid electricity. This can lead to significant savings on electricity bills over time.
- Grid Backup Capability: Hybrid systems can be configured to seamlessly switch between solar, battery, and grid power as needed. This provides added resilience and ensures continuous power supply, even during extended periods of low solar production or battery depletion.
- Environmental Benefits: Like all solar power systems, hybrid systems generate clean, renewable energy from sunlight, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This helps combat climate change and contributes to a more sustainable future.
Off-Grid Solar Power System
An off-grid solar power system, also known as a standalone system, operates independently of the electrical grid, providing electricity to remote locations or properties without access to utility power.
- Solar Panels: Off-grid systems rely on solar panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through photovoltaic technology. These panels are typically mounted on rooftops or ground-mounted arrays to maximize exposure to sunlight.
- Battery Storage: Off-grid systems incorporate battery storage to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use during periods of low sunlight or at night. Deep-cycle batteries, such as lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries, are used to store solar-generated electricity for later use.
- Charge Controller and Inverter: A charge controller regulates the flow of electricity between the solar panels and batteries, preventing overcharging or deep discharging of the batteries. An inverter converts the DC electricity stored in the batteries into AC electricity, which can power household appliances and electronic devices.
- Backup Generator (Optional): In some off-grid systems, a backup generator may be included to provide additional power during extended periods of low sunlight or when energy demand exceeds the capacity of the solar panels and batteries. This ensures an uninterrupted power supply, especially during cloudy days or winter months.
- Energy Management System: Off-grid systems require careful energy management to ensure reliable power supply and optimize battery performance. Energy monitoring systems may be used to track energy production, consumption, and battery status, allowing users to adjust their energy usage accordingly.
- Energy Independence: Off-grid systems provide complete energy independence by allowing users to generate, store, and consume their own electricity onsite, without relying on the grid. This is particularly advantageous for remote or rural locations where grid connection is unavailable or cost-prohibitive.
- Remote Power Access: Off-grid systems enable access to electricity in remote or off-grid areas where traditional utility infrastructure is not available. This makes them ideal for powering cabins, cottages, RVs, boats, and other remote dwellings or structures.
- Reliable Power Supply: Off-grid systems offer a reliable source of electricity, even in areas prone to grid outages or disruptions. With battery storage, users can store excess solar energy for use during periods of low sunlight or inclement weather, ensuring an uninterrupted power supply.
- Environmental Sustainability: Like all solar power systems, off-grid systems generate clean, renewable energy from sunlight, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This contributes to environmental sustainability and helps combat climate change.
- Cost Savings: While the initial upfront cost of installing an off-grid solar power system may be higher than grid-connected systems, users can realize long-term cost savings by eliminating monthly electricity bills and reducing reliance on expensive diesel or gasoline generators.
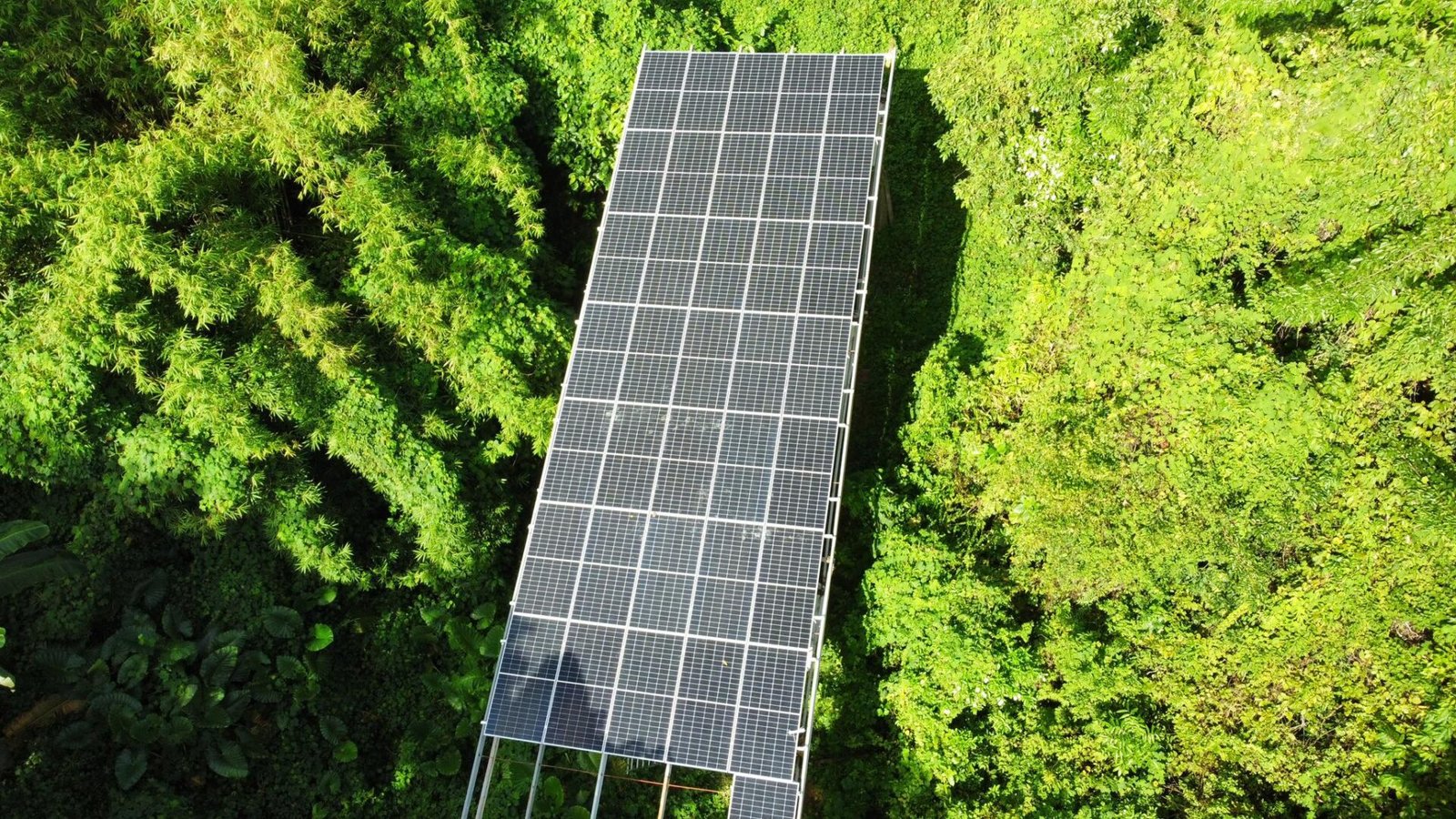
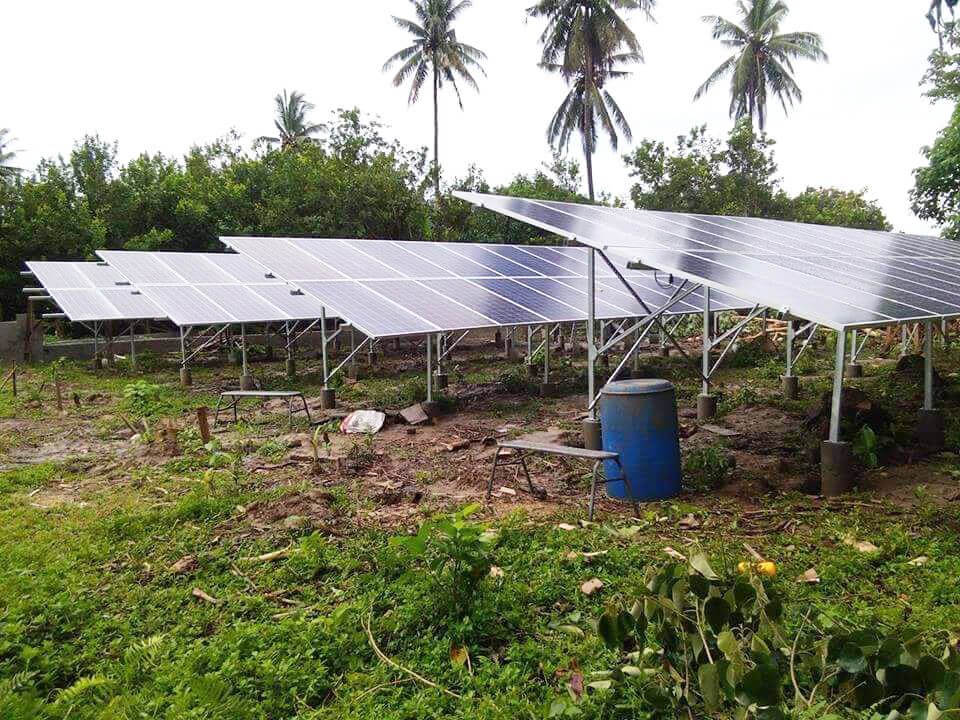


Solar Irrigation System
A solar irrigation system harnesses solar energy to power water pumps used for agricultural irrigation. It utilizes photovoltaic (PV) panels to convert sunlight into electricity, which is then used to pump water from a water source, such as a well, river, or reservoir, to irrigate crops.
- Solar Panels: Solar panels, typically mounted on ground-based racks or rooftops, capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. The panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, which is then fed into the system’s components.
- Water Pump: The solar-generated electricity powers a water pump, which draws water from a water source and pumps it through irrigation pipes or channels to the fields or crops. The type of pump used depends on factors such as water source depth, flow rate requirements, and irrigation system design.
- Controller and Sensors: A controller regulates the operation of the water pump, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Sensors may be used to monitor water levels, soil moisture, and other environmental factors, allowing for precise irrigation scheduling and water management.
- Storage Tank (Optional): In some solar irrigation systems, a storage tank may be incorporated to store water during periods of peak sunlight or when irrigation demand is low. This stored water can then be used later for irrigation when sunlight is insufficient or during nighttime hours.
- Drip or Sprinkler Irrigation: Solar irrigation systems can be configured for different types of irrigation methods, including drip irrigation, which delivers water directly to the base of plants, or sprinkler irrigation, which distributes water over the entire field in a uniform pattern.
- Cost Savings: Solar irrigation systems offer significant cost savings compared to diesel or electric-powered pumps, as they eliminate the need for expensive fuel or grid electricity. Once installed, solar pumps have minimal operating costs and can provide reliable irrigation at a lower cost per unit of water pumped.
- Energy Independence: By relying on solar energy, farmers can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and grid electricity, providing greater energy security and resilience, especially in remote or off-grid agricultural areas.
- Environmental Sustainability: Solar irrigation systems generate clean, renewable energy from sunlight, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impact compared to conventional pumps powered by fossil fuels. They also help conserve water by optimizing irrigation efficiency and reducing water waste.
- Increased Crop Yield and Quality: Consistent and reliable irrigation provided by solar pumps can enhance crop growth, yield, and quality, particularly in areas with unreliable or insufficient water supply. Proper irrigation management ensures that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time, promoting healthy plant development and optimal yields.
- Rural Development: Solar irrigation systems can contribute to rural development by improving access to water for agriculture, empowering smallholder farmers, and supporting livelihoods in rural communities. They can also facilitate sustainable agricultural practices, income generation, and food security, ultimately contributing to poverty alleviation and economic growth.